I blog about anything I find interesting, and since I have a lot of varied interests, my blog entries are kind of all over the place. You can browse my tags to sort them by topic and see which ones I frequently write about, or the archive has a complete history of my posts, dating back to 2008!
Besides my blog, I have pages for my creative projects, which are linked to on the navigation bar.
I write a lot about Linux and Android, Minecraft, and I like to rant about stuff. Generally anything that makes me curious. Also check out my Bookmarks for all sorts of cool websites about various topics I'm interested in.
For the geeks: this website respects your privacy and doesn't run any third party ads or analytics. This site speaks HTTP and doesn't require any JavaScript to work.
Getting started with BlueskyI had originally written this post on my NSFW blog back around May of this year. With the recent surge of interest in Bluesky, I thought I would copy it over here to my tech blog to give it some wider visibility.
Bluesky is a very interesting app, and it is different in some important ways to Twitter and the others that came before it.
Bluesky will not enshittify over time like its predecessors have. On the surface, it appears to be "just another Twitter" but the real interesting technology is happening under the hood. Bluesky is being developed in such a way that Bluesky (the corporation) can let go of it and allow it to be distributed as an open source, open standard network that is not under the control of a single corporation who could one day destroy it.
Below I will paste my original blog post with some of the NSFW paragraphs edited out for the different audience that I have on Kirsle.net.
I've been on Bluesky for about 4 months now and have learned a bit more about how it works and I find it rather interesting, so I thought I'd write about it and give some advice on how to get started and especially how to find your fellow nudists & exhibitionists there. So, in a similar spirit to my Getting started with Mastodon post, I'll write about Bluesky especially for an audience of people who aren't already using it. And even if you are already on Bluesky, maybe you'll learn something cool from this post anyway!
Compared to Mastodon, getting started on Bluesky is fairly simple right now: there is only one front-end web server available so far, at https://bsky.app/ where you can go and sign up in a familiar way like any other site you've used. Bluesky intends to support federated instances in the future (and they've made some good progress on that, so far), which I'll get into below, but for now at least you can avoid the choice paralysis of needing to find a server to sign up on like you have with Mastodon.
In this post I'll tell you about how content discovery works, how adult content is tagged and how to find your people to follow. And I'll also go into what's especially interesting about the way that Bluesky works as compared to Mastodon and the rest of the related fediverse.
First, let's address the elephant in the room. On Mastodon, the general sentiment about Bluesky is one of negative skepticism, and many people on Mastodon talk shit about Bluesky and compare it to Twitter. After Elon Musk took over Twitter and started making a lot of people very upset, a lot of them flocked over to Bluesky and the folks on Mastodon say things like "you're moving from one platform created by a billionaire, to another platform created by a billionaire, and you think this time it's going to be different? Have you learned nothing?"
Well, to that I say: this time it absolutely can be different, because Bluesky is not just another centralized website controlled by a corporation in the way that Twitter (and Facebook, Instagram, etc.) are. The key technology behind Bluesky is called the AT Protocol which is being developed and released as an open source standard for federated web services, and Bluesky is only one app that runs on the AT Protocol. The thing with an open standard is that everybody can participate in it, and people can write their own custom apps that use it, and they can all inter-operate with all the other apps using it, and once that's out in the wild there is no controlling it or governing it from the top down.
Mastodon is a good example of this: the server-to-server language behind the scenes on Mastodon is called ActivityPub - it's what allows Mastodon servers to be hosted by many different organizations or individuals and still allow you to follow and comment on people anywhere else. And Mastodon is far from the only ActivityPub app: Pixelfed and PeerTube are just a couple of other examples. So, despite the origin of Bluesky having been started by a billionaire as an internal project at Twitter, the technology they are building to run it on is to be a distributed open standard.
The problems we faced with centralized sites like Twitter, where a change in ownership or a pivot in business strategy left all their users held hostage, aren't nearly as possible with federated services like Mastodon because you can simply move to a server run by somebody you trust better. There's no way it can be enshittified from the top-down in the way a centralized platform will be.
Now, it is fair to remain skeptical of Bluesky until full federation and open-source self-hosting becomes possible. They are actively developing the AT Protocol and, while third-party developers are already writing code to support it, the system is not fully open and ready yet. The down side of building an open standard is that, once it's out there, you've lost control of the direction it will evolve. It's important to design it the best as you can in the beginning, which is why Bluesky has been going at such a slow pace. But, they've been continually making good progress: it is now possible to self-host your data on your own server and complete data migration of your account to your own server is working (and is much more fully featured than a Mastodon account migration, which I'll get more into below).
So, let's get into the user experience of Bluesky. You've created a new account and have a lot of questions, like: how do I find people to follow? How is "adult content" tagged and discovered?
One thing that I noticed pretty quickly was that hashtags don't exist on Bluesky (though I've seen some screenshots to suggest this feature is 'coming soon', edit: we have them now). I would post some of my nudes, though, and get followed by random people and I didn't know how they were even discovering my page, especially if my recent post hadn't yet been reblogged by any of my followers!
Instead of hashtags, Bluesky has a featured called "feeds." When you sign up an account, they'll suggest a few feeds for you to discover, themed around various topics. I followed a few feeds with names like: Science, Astronomy, Developers, and Fungi Friends.
I don't know how feeds are created, but it seems that a developer somewhere had to write some code to create a feed. You don't need to worry about that, though: if you find the feed you can simply follow it/add it to your home timeline and be able to see the posts that the feed has discovered.
[redacted] Here are a few NSFW/adult content-oriented feeds I have found, if you're an exhibitionist like me and want to find your people there:
You may need to go to your "Settings -> Moderation -> Content Filters" to enable adult content if you like to see that stuff. 😈
Sharing a post on Bluesky should be very familiar compared to Twitter or anything else you've used. You can write some text and attach some pictures.
A couple of notable aspects of sharing a post that I want to highlight are:
I highly recommend writing alt texts because: those "Feeds" that help others discover your post will see your alt texts as well. When I wondered how people were discovering my posts without any hashtags, that was how. You don't need to spam a bunch of hashtags in your posts like you did on Twitter, you can just graphically describe what is shown in your pictures and be picked up on the relevant feeds for people who want to see that stuff.
And also: describing nude pictures in writing is just a very fun exercise in itself. 😈
I should also share some of the current lack of features or quirks about Bluesky that you may want to know about here.
Issues like these seem to be on the radar of the Bluesky/AT Protocol developers and may be improved upon in the future. For me personally, they are non-issues: I've always treated my Twitter (etc.) page as fully public, I've rarely ever had to block anybody, and for DMs you have always been better off taking your conversations to proper chat platforms anyway.
I think I should elaborate on that last point: Mastodon has Direct Message support but their web interface is clear that DMs on Mastodon are not secure. They say that because a DM needs to be synced to the other server your friend is on, and your server admins on both sides do have the technical capability to look in their database and read your DMs. New users on Mastodon are surprised about this, but guess what: this has always been the status quo even on centralized sites like Twitter. Whoever runs the server and database has always been able to read your DMs if they so chose to, unless your DMs are explicitly "end-to-end encrypted," which they usually have not been.
I don't know how Bluesky will implement DMs, but they seem to share this concern and (I suspect) they will bring DMs only when they are able to end-to-end encrypt them properly, which is a hard problem to solve for website-based applications, for reasons I won't get into here.
But anyway, if you're one who liked to run a "private" page where almost nobody but your friends can see your posts, etc., I thought it fair to point out how Bluesky currently works in that regard.
Mastodon and ActivityPub more generally are interesting, but I wrote before about some of the pain points and issues I have with it.
The good news is, Bluesky and the AT Protocol address some of the biggest pain points in ways that I find very interesting. In fact, the whole reason that they are developing the AT Protocol to begin with is because they found ActivityPub to have fundamental limitations that were at odds to their vision of how much better an open, federated social network could be.
A couple of examples in particular of the pain points with Mastodon include:
On Mastodon, if you no longer like your current server and want to move, you can "migrate" your account to a new place. However, this doesn't work the way that most people would hope: only your followers are moved over, but not your posts, and not the list of people who you follow.
Migrating to a new Mastodon host is basically like starting over with a fresh new account. The only nice thing that Mastodon migration does for you is to automatically move your followers, so you don't need to tell them about your new profile and they'll update to follow it automatically. Usually. Your mileage may vary with non-Mastodon software and you still might lose some followers in the move.
One of my #1 top favorite features of sites like Tumblr or Twitter was how I could write a bunch of posts over many years, and at any time, somebody who newly discovers my page was able to scroll all the way back on my timeline, if they wanted, and easily see everything I had ever posted before.
On Mastodon, this usually doesn't work very well: following somebody on Mastodon is more like subscribing to their newsletter. Your local server will show you their new posts going forward from the moment you began following them, but chances are very good that your local server does not know about their old posts from before. The only time their older posts may be available, is if your local server already knew about them before (e.g., because somebody else on your server also follows them, and so has been bringing in their posts). This is a fundamental problem with ActivityPub more generally: it is an "inbox/outbox" based protocol and there lacks a standard method to deeply retrieve historical posts from another server.
On Mastodon, it is a common experience that somebody follows you and you visit their profile, and only see maybe a couple of posts, and a notice that says "Older posts from this user are not available, click here to go to their Mastodon server to see their full page." That would be okay, but if that user is primarily NSFW and all their posts are nudity/porn, it becomes very tedious to scroll back through their page: you need to click to reveal every single blurred picture, because you probably don't have a local Mastodon account on their server, so you can't have an "automatically show me NSFW content" setting there. Speaking for me personally, I never dig very deep into somebody's page on Mastodon if I need to put up with all of that.
As I mentioned on my Fediverse pain points post, moderation on Mastodon is handled at the server level: your local server administrator makes decisions about how to moderate content coming from other servers, in ways that can harm their local users if these decisions are not ones that you would agree with. And as an end user, your only recourse then is to migrate your account to some other Mastodon server, run by somebody you like better, or to self-host your own Mastodon server where you get to decide on these things.
In an ideal world, this would be OK: since Mastodon is open source and anybody can run a server, sometimes those servers will be home to terrible people, such as racists or transphobes or general assholes. Your server admin being able to wholesale ban these servers keeps you and the rest of your users safe. But sometimes, server bans are put in for absolutely stupid reasons, personal beef between two server admins, over drama that you don't really care about, and now because a server block was put in place, you are cut off from your friends who had accounts on the other server.
The only way you avoid getting caught as collateral damage in moderator drama like this, is to self-host your own personal server yourself, where you alone get to make these moderator decisions, but that comes with its own helping of downsides: needing to have the technical skills to run a server correctly, not having a local timeline of like-minded users to discover, etc.
Recently, Bluesky has open sourced their Personal Data Server code which allows you to self-host your data on your own machine, instead of hosting it on Bluesky-managed servers. Along with the PDS, you are able to migrate your account from Bluesky's servers onto your own.
Bluesky migrations are full data migrations. They don't just move your followers like Mastodon does, it will deeply migrate all of your data: your complete timeline of posts and their attached images, and everything. This is what Mastodon users hoped for when they saw there was an ability to migrate to other servers when needed, but Mastodon fell far short of user expectations here.
And, Bluesky solves the timeline problem here too. My account is all hosted on the main Bluesky server, but I follow some self-hosting enthusiasts who've already set up their own PDS servers, and I can view their profile page within Bluesky's (bsky.app) web interface, and I can scroll all the way back to the beginning of their timelines if I want to, and I don't have to click to reveal all their NSFW images because I'm viewing them from the server my account is on, where I have opted-in to see adult content without blurring. So again here, Bluesky's style of federation does what I would hope for and expect Mastodon to do, but which Mastodon does not do.
And finally, Bluesky puts moderator decisions in the hands of users where it belongs. Admittedly, moderating 'the entire Internet' is a big job and most people don't really want this responsibility, so Bluesky has "moderator lists" where you can choose to follow somebody else's list if you like theirs. So if you want to keep yourself shielded from terrible people, you can follow somebody's moderation list where they do that job for you. But if they make decisions you don't like, or they cut you off from your friends on accident, you can fix that yourself by changing which lists you follow. You avoid inter-admin drama over silly nonsense you don't care about that way. For a bit more reading, here is a recent Bluesky blog post about moderation.
Identity regards your username or how people discover you in the app.
On Mastodon, your identity is tied closely to the Mastodon server you signed up on. If you signed up on the server "mstdn.social" your Mastodon handle looks like "@yourname@mstdn.social". If I want somebody to follow me on Mastodon, I give them that full identity handle and they paste it into their search bar to bring me up.
The down side comes when I want to migrate to another server: my identity will change! My first Mastodon profile was @redacted@mastodon.social because I signed up on the mastodon.social server. I've migrated a few times since then, which always gave me a new identity. I was able to move (most) of my followers each time, so they didn't really need to care that much, but I did need to update my blog and find/replace all the places I linked to my profile and update to the new location.
On Bluesky, identity is de-coupled from the server you signed up on. They rely on the tried and true Domain Name System for identity. For most Bluesky users, they have names that look like soandso.bsky.social where they have the "bsky.social" domain in their handle. This may be OK for most people who don't own their own custom domain names, but you don't have to have a .bsky.social handle. My handle on Bluesky is my blog's domain name: @kirsle.net. If you have your own domain name, you can use it as your Bluesky handle, and then you never need to worry about changing it, even if you migrated to a different Bluesky server in the future!
And even if you have a .bsky.social handle now: you could keep that handle even if you migrate servers, too. But if you were interested in self-hosting your data, getting your own domain name is the most sure way to make sure you're always in charge of your identity.
Should you check out Bluesky, my profile link is at https://bsky.app/profile/kirsle.net and you can give me a follow.
I think that'll do it for today, until I have any more exciting news about Bluesky (probably when they make further advancements towards allowing open federation and full self-hosting). When the dust settles with all of that, I plan on setting up my own Bluesky servers for myself! 😎
A while back (February 2023) I built an open source webcam chat room for one of my side project websites.
It was very much designed to resemble those classic, old school Adobe Flash based webcam chat rooms: where it is first and foremost a text based chat (with public channels and private messages), and where some people could go on webcam and they could be watched by other people in the chat room, in an asynchronous manner.
It didn't take terribly long to get the chat room basically up and running, and working well, for browsers such as Chrome and Firefox - but it was a whole other story to get it to work as well for Apple's web browsers: Safari, and iPads and iPhones.
This blog post will recount the last ~year and change of efforts to get Safari to behave nicely with my chat room, and the challenges faced and lessons learned along the way.
First, it will be helpful to describe the basic features of the chat room and how I designed it to work, to set some context to the Safari specific challenges I faced along the way.
There are a few other features on top of these, but the above are the basic fundamentals that are relevant to this story about getting this all to work on Safari.
The additional features include:
The underlying web browser standard that allows videos to be shared at all is called WebRTC, which stands for "Web Real Time Communication." It is supported in all major web browsers, including Safari, but the devil is in the details.
WebRTC basically enables two web browsers to connect to each other, directly peer-to-peer, and exchange data (usually, video and audio data but any kind of data is possible). It can get two browsers to connect even when both sides of the connection are behind firewalls or behind a NAT (as 99% of regular home Internet users are).
For my chat room, it means that webcam data is sent directly between the chat users and none of it needs to pass through my server (which could be expensive for me to pay for all that bandwidth!).
It's a rather complex, and poorly documented, system but for the sake of this blog post, I will try and distill it down to its bare essence. The following is massively simplified, but if curious to dive in to the weeds on it, the best resource I found online is this free e-book: WebRTC for the Curious.
When two users are logged on to my chat room, and one wants to open the other's camera, the basic ingredients that make the WebRTC magic work includes:
The signaling server in WebRTC is much simpler than it sounds: it is really just any server you write which is capable of passing messages along, back and forth between the two parties who want to connect. It could be a WebSocket server, it could be based on AJAX requests to a PHP script, it could even be printed out on a post card and delivered by snail mail (though that way would take the longest).
For my chat room's use case, I already had a signaling server to use: my WebSockets server that drives the rest of the chat room.
The server side of the chat room was a WebSockets server, where users would post their chat messages and the server would broadcast those back out to everybody else, and the server would push "Who's Online" list updates, etc. - so I just added support for this same WebSockets server to allow forwarding WebRTC negotiation messages between the two users.
There are a couple of important terms used in WebRTC that are not super intuitive at first glance.
The two parties of a WebRTC connection are named the Offerer and the Answerer.
Both the Offerer and the Answerer are able to attach data channels to their side of the connection. Most obviously, the Answerer will attach their active webcam feed to the connection, so that the Offerer (who wanted to watch it) is able to receive it and show it on their screen.
The Offerer is also able to attach their own camera to that opening connection, as well, and their video data will be received automatically on the Answerer's side once the connection is established. But, more on that below.
So, going back to the original design goals of my chat room above, I wanted video sharing to be "asynchronous": it must be possible for Alice, who is not sharing her video, to be able to watch Bob's video in a one-directional manner.
The first interesting thing I learned about WebRTC was that this initially was not working!
So the conundrum at first, was this: I wanted Alice to be able to receive video, without sharing her own video.
I found that I could do this by setting these parameters on the initial offer that she creates:
pc.createOffer({
offerToReceiveVideo: true,
offerToReceiveAudio: true,
});
Then Alice will offer to receive video/audio channels despite not sharing any herself, and this worked OK.
But, I came to find out that this did not work with Safari, but only for Chrome and Firefox!
I learned that there were actually two major iterations of the WebRTC API, and the above hack was only supported by the old, legacy version. Chrome and Firefox were there for that version, so they still support the legacy option, but Safari came later to the game and Safari only implemented the modern WebRTC API, which caused me some problems that I'll get into below.
So, in February 2023 I officially launched my chat room and it worked perfectly on Firefox, Google Chrome, and every other Chromium based browser in the world (such as MS Edge, Opera, Brave, etc.) - asynchronous webcam connections were working fine, people were able to watch a webcam without needing to share a webcam, because Firefox and Chromium supported the legacy WebRTC API where the above findings were all supported and working well.
But then, there was Safari.
Safari showed a handful of weird quirks, differences and limitations compared to Chrome and Firefox, and the worst part about trying to debug any of this, was that I did not own any Apple device on which I could test Safari and see about getting it to work. All I could do was read online (WebRTC stuff is poorly documented, and there's a lot of inaccurate and outdated information online), blindly try a couple of things, and ask some of my Apple-using friends to test once in a while to see if anything worked.
Slowly, I made some progress here and there and I'll describe what I found.
The first problem with Safari wasn't even about WebRTC yet! Safari did not like my WebSockets server for my chat room.
What I saw when a Safari user tried to connect was: they would connect to the WebSockets server, send their "has entered the room" message, and the chat server would send Safari all the welcome messages (listing the rules of the chat room, etc.), and it would send Safari the "Who's Online" list of current chatters, and... Safari would immediately close the connection and disconnect.
Only to try and reconnect a few seconds later (since the chat web page was programmed to retry the connection a few times). The rest of the chatters online would see the Safari user join/leave, join/leave, join/leave before their chat page gave up trying to connect.
The resolution to this problem turned out to be: Safari did not support compression for WebSockets. The WebSockets library I was using had compression enabled by default. Through some experimentation, I found that if I removed all the server welcome messages and needless "spam", that Safari was able to connect and stay logged on -- however, if I sent a 'long' chat message (of only 500 characters or so), it would cause Safari to disconnect.
The root cause came down to: Safari didn't support WebSocket compression, so I needed to disable compression and then Safari could log on and hang out fine.
So, finally on to the WebRTC parts.
Safari browsers were able to log on to chat now, but the WebRTC stuff simply was not working at all. The Safari user was able to activate their webcam, and they could see their own local video feed on their page, but this part didn't involve WebRTC yet (it was just the Web Media API, accessing their webcam and displaying it in a <video> element on the page). But in my chat room, the Safari user was able to tell the server: "my webcam is on!", and other users would see a clickable video button on the Who List, but when they tried to connect to watch it, nothing happened.
So, as touched on above, WebRTC is an old standard and it had actually gone through two major revisions. Chrome and Firefox were there for both, and they continue to support both versions, but Safari was newer to the game and they only implemented the modern version.
The biggest difference between the old and new API is that functions changed from "callback based" into "promise based", e.g.:
// Old API would have callback functions sent as parameters
pc.setLocalDescription(description, onSuccess, onFailure);
// New API moved to use Promises (".then functions") instead of callback functions
pc.setLocalDescription(description).then(onSuccess).catch(onFailure);
The WebRTC stuff for Safari wasn't working because I needed to change these function calls to be Promise-based instead of the legacy callback function style.
By updating to the modern WebRTC API, Safari browsers could sometimes get cameras to connect, but only under some very precise circumstances:
This was rather inconvenient and confusing to users, though: the Safari user was never able to passively watch somebody else's camera without their own camera being on, but even when they turned their camera on first, they could only open about half of the other cameras on chat (only the users who wanted to auto-open Safari's camera in return).
This was due to a couple of fundamental issues:
offerToReceiveVideo: true option), which Safari did not support.
For a while, this was the status quo. Users on an iPad or iPhone were encouraged to try switching to a laptop or desktop PC and to use a browser other than Safari if they could.
There was another bug on my chat room at this point, too: the Safari browser had to be the one to initiate the WebRTC connection for anything to work at all. If somebody else were to click to view Safari's camera, nothing would happen and the connection attempt would time out and show an error.
This one, I found out later, was due to the same "callback-based vs. promise-based" API for WebRTC: I had missed a spot before! The code path where Safari is the answerer and it tries to respond with its SDP message was using the legacy API and so wasn't doing anything, and not giving any error messages to the console either!
At this stage, I still had no access to an Apple device to actually test on, so the best I could do was read outdated and inaccurate information online. It seems the subset of software developers who actually work with WebRTC at this low of a level are exceedingly rare (and are all employed by large shops like Zoom who make heavy use of this stuff).
I had found this amazing resource called Guide to WebRTC with Safari in the Wild which documented a lot of Safari's unique quirks regarding WebRTC.
A point I read there was that Safari only supported two-way video calls, where both sides of the connection are needing to exchange video. I thought this would be a hard blocker for me, at the end of the day, and would fly in the face of my "asynchronous webcam support" I wanted of my chat room.
So the above quirky limitations: where Safari needed to have its own camera running, and it needed to attach it on the outgoing WebRTC offer, seemed to be unmoveable truths that I would have to just live with.
And indeed: since Safari didn't support offerToReceiveVideo: true to set up a receive-only video channel, and there was no documentation on what the modern alternative to that option should be, this was seeming to be the case.
But, it turned out even that was outdated misinformation!
Seeing what Safari's limitations appeared to be, in my chat room I attempted a sort of hack, that I called "Apple compatibility mode".
It seemed that the only way Safari could receive video, was to offer its own video on the WebRTC connection. But I wanted Safari to at least, be able to passively watch somebody's camera without needing to send its own video to them too. But if Safari pushed its video on the connection, it would auto-open on the other person's screen!
My hacky solution was to do this:
But, this is obviously wasteful of everyone's bandwidth, to have Safari stream video out that is just being ignored. So the chat room would only enable this behavior if it detected you were using a Safari browser, or were on an iPad or iPhone, so at least not everybody was sending video wastefully all the time.
Recently, I broke my old laptop on accident when I spilled a full cup of coffee over its keyboard, and when weighing my options for a replacement PC, I decided to go with a modern Macbook Air with the Apple Silicon M3 chip.
It's my first Apple device in a very long time, and I figured I would have some valid use cases for it now:
The first bug that I root caused and fixed was the one I mentioned just above: when somebody else was trying to connect in to Safari, it wasn't responding. With that bug resolved, I was getting 99% to where I wanted to be with Safari support on my chat room:
The only remaining, unfortunate limitation was: the Safari user always had to have its local webcam shared before it could connect in any direction, because I still didn't know how to set up a receive-only video connection without offering up a video to begin with. This was the last unique quirk that didn't apply to Firefox or Chrome users on chat.
So, the other day I sat down to properly debug this and get it all working.
I had to find this out from a thorough Google search and landing on a Reddit comment thread where somebody was asking about this question: since the offerToReceiveVideo option was removed from the legacy API and no alternative is documented in the new API, how do you get the WebRTC offerer to request video channels be opened without attaching a video itself?
It turns out the solution is to add what are called "receive-only transceiver" channels to your WebRTC offer.
// So instead of calling addTrack() and attaching a local video:
stream.getTracks().forEach(track => {
pc.addTrack(track);
});
// You instead add receive-only transceivers:
pc.addTransceiver('video', { direction: 'recvonly' });
pc.addTransceiver('audio', { direction: 'recvonly' });
And now: Safari, while not sharing its own video, is able to open somebody else's camera and receive video in a receive-only fashion!
At this point, Safari browsers were behaving perfectly well like Chrome and Firefox were. I also no longer needed that "Apple compatibility mode" hack I mentioned earlier: Safari doesn't need to superfluously force its own video to be sent on the offer, since it can attach a receive-only transciever instead and receive your video normally.
There were really only two quirks about Safari at the end of the day:
And that second bit ties into the first: the only way I knew initially to get a receive-only video connection was to use the legacy offerToReceiveVideo option which isn't supported in the new API.
And even in Mozilla's MDN docs about createOffer, they point out that offerToReceiveVideo is deprecated but they don't tell you what the new solution is!
One of the more annoying aspects of this Safari problem had been, that iPad and iPhone users have no choice in their web browser engine.
For every other device, I can tell people: switch to Chrome or Firefox, and the chat works perfectly and webcams connect fine! But this advice doesn't apply to iPads and iPhones, because on iOS, Apple requires that every mobile web browser is actually just Safari under the hood. Chrome and Firefox for iPad are just custom skins around Safari, and they share all its same quirks.
And this is fundamentally because Apple is scared shitless about Progressive Web Apps and how they might compete with their native App Store. Apple makes sure that Safari has limited support for PWAs, and they do not want Google or Mozilla to come along and do it better than them, either. So they enforce that every web browser for iPad or iPhone must use the Safari engine under the hood.
Recently, the EU is putting pressure on Apple about this, and will be forcing them to allow competing web browser engines on their platform (as well as allowing for third-party app stores, and sideloading of apps). I was hopeful that this meant I could just wait this problem out: eventually, Chrome and Firefox can bring their proper engines to iPad and I can tell my users to just switch browsers.
But, Apple isn't going peacefully with this and they'll be playing games with the EU, like: third-party app stores and sideloading will be available only to EU citizens but not the rest of the world. And, if Apple will be forced to allow Chrome and Firefox on, Apple is more keen to take away Progressive Web App support entirely from their platform: they don't want a better browser to out-compete them, so they'd rather cripple their own PWA support and make sure nobody can do so. It seems they may have walked back that decision, but this story is still unfolding so we'll see how it goes.
At any rate: since I figured out Safari's flavor of WebRTC and got it all working anyway, this part of it is a moot point, but I include this section of the post because it was very relevant to my ordeal of the past year or so working on this problem.
Early on with this ordeal, I was thinking that Safari's implementation of WebRTC was quirky and contrarian just because they had different goals or ideas about WebRTC. For example, the seeming "two-way video calls only" requirement appeared to me like a lack of imagination on Apple's part: like they only envisioned FaceTime style, one-on-one video calls (or maybe group calls, Zoom style, where every camera is enabled), and that use cases such as receive-only or send-only video channels were just not supported for unknowable reasons.
But, having gotten to the bottom of it, it turns out that actually Safari was following the upstream WebRTC standard to a tee. They weren't there for the legacy WebRTC API like Firefox and Chrome were, so they had never implemented the legacy API; by the time Safari got on board, the modern API was out and that's what they went with.
The rest of it came down to my own lack of understanding combined with loads of outdated misinformation online about this stuff!
Safari's lack of compression support for WebSockets, however, I still hold against them for now. 😉
If you ever have the misfortune one day to work with WebRTC at a low level like I have, here are a couple of the best resources I had found along the way:
I frequently have pretty vivid, detailed and crazy dreams and when I have a particularly interesting one, I write it down in my dream journal. The one I awoke from this morning left such a strong impression on me that I also feel like sharing it here on my blog!
It involves artificial intelligence, humanoid robots and morally bankrupt billionaire corporations. I like to think I can tell a good story, so I hope you'll check this one out!
So at the start of this dream, I had received a mysterious package in the mail. It was a medium sized box, maybe three feet tall, and had no return address but it was addressed to me, and it wasn't anything that I ordered myself.
Inside the box was a humanoid robot, covered in sleek white panels and looking like something that Apple might design. I powered it on, and it was able to speak with me in plain English and seemed to have a level of intelligence on par with ChatGPT. It had arms and legs and a robot face and everything. Presumably it could walk and move around as well. When it would enter an idle mode (maybe to recharge), it would "turtle up" and retreat into its shell, taking up less space in the room, a few feet tall. When standing, it was the size of a small adult human, maybe 5 feet tall or so.
An A.I. generated image of what this robot may have looked like, created on deepai.org.
On a different day in this dream, I was hanging out in the living room and I had a couple of friends over, and the robot was in its idle pose nearby. Suddenly, the robot whirred to life, and panels on its body opened up, and then I can only describe that it 'attacked' me. Out of these panels, a bunch of wires shot out quickly, some with needles on the ends, which all found their way to my body. One such needle went into my arm, into a vein, reminiscient of when you are put on an IV drip at a hospital. I don't remember where the other wires landed.
The robot then injected me with something: tiny little machines. Some of them assembled themselves together inside my body, forming a larger disc shaped structure a couple of inches across, and I could see it move around under my skin and could feel it if I touched it. Most of the other tiny machines navigated their way through my veins, arteries and other ducts in my body.
I could feel all of these things moving around, and especially around my lower abdomen. I've never experienced having kidney stones before, but I imagine it could be similar, though instead of painful, the movement felt ticklish and highly sensitive, similar to post-orgasm sensitivity, as they worked their way around my body.
Naturally, I was freaking the fuck out, but I was also afraid to respond too violently to all of this in case I broke the robot and left its work in a half-complete state, which could result in a much worse outcome for me. My friends in the room with me were watching all this happen and they were shocked and didn't know what to do either.
During this time, the robot was unresponsive and didn't respond to any voice commands. It was in its idle pose, but clearly busy computing something, with lights on its chassis flashing and everything.
After no more than 10 minutes or so, the robot was done and it disengaged from my body, retracting all the wires and tools back into itself, closing its panels and then transforming into its humanoid social form to talk to me.
Of course, I asked it what the fuck just happened. It explained to me that it is a healthcare robot and it had just finished giving me an examination. It told me I had some plaque buildup in my arteries that it cleaned out for me, and that while my kidneys were in the range of normal healthy function, they were a bit on the lower end of that range (whatever that meant).
Naturally, I had a whole lot of questions. This robot was made from some highly sophisticated technology that I had never seen the likes of before.
I asked it who built it. The robot replied that it was created by a major multi-billion dollar pharmaceutical company. It told me the name of the company, though I don't remember it now.
I asked it why it was delivered to my house. It explained that the company who created it was facing some problems: they weren't cleared yet to begin human trials on the new technology, and they were facing fines or regulations and were at risk of going bankrupt or forced to shut down. They mailed these units out for free to random people as a way to circumvent the law, get some human test subjects, and (hopefully) prove that the machine is safe and effective. I was just one of the "lucky" ones who received one of these units.
I asked the robot whether I can opt-out of their test program, and the robot said I could not. In the room with us was a small figurine of Baymax from Big Hero 6. I picked it up and showed it to the robot and said: "in the movie Big Hero 6, they had healthcare robots and you could say to the robot 'I am satisfied with my care' and they will power down and stay that way" and the robot told me that that wouldn't work on it, and that it was designed for long-term active care.
I asked the robot whether I could tell people about all of this - I had a good mind to, at the very least, write about this experience on my blog. It strongly advised against me telling anybody about it. It didn't threaten me or tell me what would happen if I disobeyed, and I know I never signed a non-disclosure agreement about this, but given the highly advanced technology it had just displayed for me, I decided I would comply with it - at least for now. But I had found the whole thing highly sketchy and unethical and was beginning to contemplate what my next steps should be, before finally waking up from this dream.
Anonymous asks:
What is your favorite memory of Bot-Depot?
Oh, that's a name I haven't heard in a long time! I have many fond memories of Bot-Depot but one immediately jumped to mind which I'll write about below.
For some context for others: Bot-Depot was a forum site about chatbots that was most active somewhere in the range of the year 2002-08 or so, during what (I call) the "first wave of chatbots" (it was the first wave I lived through, anyway) - there was an active community of botmasters writing chatbots for the likes of AOL Instant Messenger, MSN Messenger, Yahoo! Messenger, and similar apps around that time (also ICQ, IRC, and anything else we could connect a bot to). The "second wave" was when Facebook Messenger, Microsoft Bot Platform, and so on came and left around the year 2016 or so.
My favorite memory about Bot-Depot was in how collaborative and innovative everyone was there: several of us had our own open source chatbot projects, which we'd release on the forum for others to download and use, and we'd learn from each other's code and make better and bigger chatbot programs. Some of my old chatbots have their code available at https://github.com/aichaos/graveyard, with the Juggernaut and Leviathan bots being some of my biggest that were written at the height of the Bot-Depot craze. Many of those programs aren't very useful anymore, since all the instant messengers they connected to no longer exist, and hence I put them up on a git repo named "graveyard" for "where chatbots from 2004 go to die" to archive their code but not forget these projects.
Most of the bots on Bot-Depot were written in Perl, and one particular chatbot I found interesting (and learned a "mind blowing" trick I could apply to my own bots) was a program called Andromeda written by Eric256, because it laid down a really cool pattern for how we could better collaborate on "plugins" or "commands" for our bots.
Many of the Bot-Depot bots would use some kind of general reply engine (like my RiveScript), and they'd also have "commands" like you could type /weather or /jokes in a message and it would run some custom bit of Perl code to do something useful separately from the regular reply engine. Before Andromeda gave us a better idea how to manage these, commands were a little tedious to manage: we'd often put a /help or /menu command in our bots, where we'd manually write a list of commands to let the users know what's available, and if we added a new command we'd have to update our /help command to mention it there.
Perl is a dynamic language that can import new Perl code at runtime, so we'd usually have a "commands" folder on disk, and the bot would look in that folder and require() everything in there when it starts up, so adding a new command was as easy as dropping a new .pl file in that folder; but if we forgot to update the /help command, users wouldn't know about the new command. Most of the time, when you write a Perl module that you expect to be imported, you would end the module with a line of code like this:
1;
And that's because: in Perl when you write a statement like require "./commands/help.pl"; Perl would load that code and expect the final statement of that code to be something truthy; if you forgot the "1;" at the end, Perl would throw an error saying it couldn't import the module because it didn't end in a truthy statement. So me and many others thought of the "1;" as just standard required boilerplate that you always needed when you want to import Perl modules into your program.
What the Andromeda bot showed us, though, is that you can use other 'truthy' objects in place of the "1;" and the calling program can get the value out of require(). So, Andromeda set down a pattern of having "self-documenting commands" where your command script might look something like:
# The command function itself, e.g. for a "/random 100" command that would
# generate a random number between 0 and 100.
sub random {
my ($bot, $username, $message) = @_;
my $result = int(rand($message));
return "Your random number is: $result";
}
# Normally, the "1;" would go here so the script can be imported, but instead
# of the "1;" you could return a hash map that describes this command:
{
command => "/random",
usage => "/random [number]",
example => "/random 100",
description => "Pick a random number between 0 and the number you provide.",
author => "Kirsle",
};
The chatbot program, then, when it imports your folder full of commands, it would collect these self-documenting objects from the require statements, like
# A hash map of commands to their descriptions
my %commands = ();
# Load all the command scripts from disk
foreach my $filename (<./commands/*.pl>) {
my $info = require $filename;
# Store their descriptions related to the command itself
$commands{ $info->{'command'} } = $info;
}
And: now your /help or /menu command could be written to be dynamic, having it loop over all the loaded commands and automatically come up with the list of commands (with examples and descriptions) for the user. Then: to add a new command to your bot, all you do is drop the .pl file into the right folder and restart your bot and your /help command automatically tells a user about the new command!
For an example: in my Leviathan bot I had a "guess my number" game in the commands folder: https://github.com/aichaos/graveyard/blob/master/Leviathan/commands/games/guess.pl
Or a fortune cookie command: https://github.com/aichaos/graveyard/blob/master/Leviathan/commands/funstuff/fortune.pl
After we saw Andromeda set the pattern for self-documenting commands like this, I applied it to my own bots; members on Bot-Depot would pick one bot program or another that they liked, and then the community around that program would write their own commands and put them up for download and users could easily download and drop the .pl file into the right folder and easily add the command to their own bots!
I think there was some effort to make a common interface for commands so they could be shared between types of chatbot programs, too; but this level of collaboration and innovation on Bot-Depot is something I've rarely seen anywhere else since then.
We had also gone on to apply that pattern to instant messenger interfaces and chatbot brains, as well - so, Leviathan had a "brains" folder which followed a similar pattern: it came with a lot of options for A.I. engine to power your bot's general responses with, including Chatbot::Alpha (the precursor to my RiveScript), Chatbot::Eliza (an implementation of the classic 1970s ELIZA bot), and a handful of other odds and ends - designed in a "pluggable", self-documenting way where somebody could contribute a new type of brain for Leviathan and users could just drop a .pl file into the right folder and use it immediately. Some of our bots had similar interfaces for the instant messengers (AIM, MSN, YMSG, etc.) - so if somebody wanted to add something new and esoteric, like a CyanChat client, they could do so in a way that it was easily shareable with other botmasters.
For more nostalgic reading, a long time ago I wrote a blog post about SmarterChild and other AOL chatbots from around this time. I was meaning to follow up with an article about MSN Messenger but had never gotten around to it!
A discussion thread I got pulled into on Mastodon had me suddenly nostalgic for something we once had on the Internet, and which was really nice while it lasted: the Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol, or XMPP, or sometimes referred to by its original name, Jabber.
What kicked off the discussion was somebody asking about a more modern "decentralized chat platform" known as Matrix (not the movie). A lot of people online talk about how they like Matrix, but I one time had a go at self-hosting my own Matrix node (which I feel I should rant about briefly, below), and the discussion turned back towards something that we used to have which was (in my opinion) loads better, XMPP.
One of the many things I get really interested in is the nature of "reality" or at least the conscious parts of it (e.g. my perception of reality). The mind is such a curious and powerful thing -- like how none of us has ever actually 'seen' Objective Reality, because our brains are trapped in our dark skulls and all we really get are electrical signals sent by our eyes and other sensors. The brain then makes up all the stuff you see and call reality: a multimedia simulation based on what your brain thinks is going on out there in the world. We've all heard questions like "is my green, your red?" and how you'll never know for sure what somebody else sees in their reality.
In recent years I have been getting into meditation and really paying attention, really studying the way my mind works and I have found a few interesting things that I haven't seen talked about much online. I am currently suspicious that there is a connection between lucid dreaming, closed-eye visuals during wakeful consciousness, and the place in between the two: psychedelic visuals, which you can apparently just meditate your way into seeing, no entheogens required.
Let's start with the easy one. When I close my eyes and look into the darkness of my eyelids, I frequently will see some shapes and colors. From what I've heard from other people, this seems fairly common - you might see these too.
My regular closed-eye visuals tend to just be vague, formless blobs of color, maybe a blue blob here and a green one there. All kind of meandering around on their own, but very low resolution. Maybe they might vaguely form a face or some recognizable shape, but just loosely -- like seeing shapes in the clouds -- nothing very exciting.
But spoiler alert: they can get much more exciting.
One night, I woke up from dreaming at maybe 3:00 in the morning (who knows), to get up and use the bathroom as one does. When I got back in bed I closed my eyes and I decided to look for my closed eye visuals (often if I'm not deliberately trying to see them, they go unnoticed by me and I think I just "see" blackness with my eyes closed).
I was expecting to see the usual amorphous blobs, but what I instead saw blew me away: my closed eye visuals (henceforth called CEVs) were breathtakingly sharp, vivid, colorful and crisp. I was seeing a colleidoscope of random images flashing before my eyes. It reminded me a lot of the Marvel movie opening logo. But every image I saw was just so crystal clear, with sharp lines and edges and vivid colors -- a far cry from the usual vague shapes my CEVs take on during the daytime.
I attribute this to the fact I had woken up from dreaming (REM sleep) and my brain was still close to that dream state. I have a suspicion that CEVs have a whole spectrum of forms they take: the vague blobbies is on one end of the spectrum, and full-color life-like hallucinations that we call "dreams" are at the opposite end.
And in between those two poles are other states that some people are familiar with.
A couple of years ago, quite by accident, I managed to meditate my way into seeing psychedelic visuals over top of reality. And you can probably learn to do this, too. I will save you the long story (I had written about it before if curious) and cut straight to the chase -- here is how I've been able to consistently pull this off on command.
The trick is to just lock your eyes onto as fine a point as you can manage, and resist the urge to twitch your eyes even as your vision begins to play tricks on you. Many of you have probably experienced this much already: you know if you stare at a thing for too long, your vision plays tricks and things start disappearing or acting weird because of the sensory satiation, and darting your eyes will "reset" your vision to normal. But try and resist the urge to dart your eyes and just let your visuals do what they shall.
What happens next for me is: I will begin to see my closed eye visuals project themselves over top of reality, with my eyes open. The blobby, amorphous shapes I see with my eyes closed appear while they're open. But then my CEVs will begin to "play off of" or interact with my reality: where the border of one of the blobs touched a ridge on my ceiling that I was staring at, the ridge would wiggle or bounce back, as if my CEVs are interacting with it.
These visuals slowly ramp up and I'll begin seeing geometric patterns, fractals, lots of colors, and as these fractals interact with the scene I am staring at, they get everything to start wiggling and dancing. It can take me about 30 minutes into my meditation before I am seeing fully, 100% authentic, height of the strongest acid or mushroom trip I'd ever been on, visuals projected out onto whatever I was staring at during my meditation.
And when I've decided I had enough: I just look somewhere else and snap! everything is back in its place, in much the same way that darting your eyes during the earliest part of all of that "resets" your vision to normal.
Tell me if this sounds familiar: when I was a kid I would sometimes be woken up from a really good dream and wished I could have stayed in my dream a little bit longer to see how it ended. I could try and "make up" the ending myself, daydream how I think it might have gone, but it never felt right -- when you're in a dream, it's like your subconscious is telling you a story, and you can't quite predict what's going to come next. There's something magical about dreams that when I try and make up the ending myself, it doesn't come out right.
Well -- and I don't know exactly when this started, but it was in recent months at least -- I have somehow gained the ability to let my imagination wander freely and I can actually let my dreams finish themselves out, autonomously, after I wake up and I'll be fully aware I'm awake (and feel my body in bed, be able to hear my surroundings) but still visually see and hear the dream at the same time.
I attribute this to my practice with meditation -- I don't know of concrete steps that someone could try (not like my previous section) but I suspect the ability to "let go" of your mind, or to just watch it and not mess with it, was a feature here. I'll give you an example of what I mean.
A couple years ago I was reading some of Carl Jung and he talked about "active imagination" where he was able to visualize a scene in his head with characters in it, and then set his imagination free, and he could interrogate the characters and ask them questions and he would get responses from them that he couldn't predict (in very much the same way as dream characters). It's different to regular conscious daydreaming where you are controlling the dialogue of all the characters. It's more like when you are dreaming, and your dream characters talk to you and you can't quite predict what they're going to say because it's a different part of your mind that controls them: your subconscious.
After reading this I was trying, and failing, to do active imagination myself. I could set up the scene, and ask my characters a question, but I always felt like it was I who was dictating their responses -- I was just daydreaming consciously with myself. I haven't yet tried active imagination again, but this ability to let my subconscious wander and finish my dreams out seems to be very close to what I was thinking here.
There's already a lot of literature out there about lucid dreaming so I won't go too deep here.
Lucid dreaming is basically when you become aware that you're dreaming. You may be having some crazy dream about something nonsensical happening and have the epiphany: "oh shit, this is a dream!" and you can have a lot of fun with it. You can decide to change anything you want about the dream, or fly through the air like Superman, or summon specific dream characters that you want to talk to. I've had a good handful of lucid dreams in my life, but never very consistently. In many cases I'll realize I'm dreaming, and then just let my dream tell its story without meddling with it too much. I've found that if I meddle too much, my dream "gives up" on its story and just gives me all the controls, and it becomes a little bit less fun for me. I have "god mode" control but much less of the dream is unpredictable or surprising then (though my dream characters are still unpredictable in what they say).
From talking to my dream characters and asking them deep and personal questions about myself, and getting surprising answers back from them, I am suspicious that talking to a dream character is the same as talking directly to my inner subconscious, in plain English.
Just thought I'd jot down some of my latest findings. I have told some friends about these and some of them have experienced similar things, if not to the same extent I have yet. I hope this may have sparked your curiosity and if others may be able to reproduce some of my findings themselves.
I have more posts like this on my #42 blog tag where I write about life, the universe, and everything. It's a lot of stuff about consciousness and occasionally spiritual stuff (the two have many likes alike, and all the characters and archetypes that Jung says are in our consciousness have mirrors in religious figures from all cultures which I also find very fascinating!)
So I haven't posted a good rant on my blog in quite some time - I had chilled out a lot in my older years, but I just have to tell this story about Safari and my struggles in getting it to work with my chat room I had built recently.
My chat room is a fairly basic app - it's open source and written "from scratch" using WebSockets to handle the client/server communication and they pass basic JSON messages around. All fairly standard stuff and shouldn't be a big ask for any modern web browser that supports modern web standards. It works flawlessly in Google Chrome as well as all other Chromium derivatives (including Edge, Brave, etc.), and it works flawlessly on Firefox, and when you run either browser on your Windows, Linux or Mac OS computer. It even works great on all Androids, too - using Chromium or Firefox browser engines.
But then there's Safari. Safari "supports" WebSockets but it doesn't do so very well and I've been fighting this for weeks now trying to chip away at this problem. Both when you run Safari on your Mac OS Ventura desktop or on your iPhone or iPad, Safari is very easy to overwhelm and it will disconnect from the chat room at the slightest hiccup of an issue.
My rant here actually is about three different problems that have made my life difficult trying to get Safari to work:
I don't own a Macbook or an iOS device and so would have no way to even debug or look into this problem, but at least there is an option to run Mac OS inside of a virtual machine (using something like OSX-KVM) so at least I can look into the desktop Safari browser and see what its deal is.
First - here is how my chat basically works: you connect, send your username to log in, the chat tells everyone you joined, sends everyone the new Who's Online roster, and sends some "welcome messages" to the one who joined where I can send my rules or new feature announcements to you.
What I would see when a Safari user logged in was: they'd connect, log in, receive all those welcome messages and then they would immediately hangup the connection and log off. On their side, the web browser gives a very unhelpful error message regarding the WebSocket:
Protocol error.
That's it - it doesn't say what the error was. Even when I have a Safari browser in front of me, they give me no help at all to find out what's wrong!
Through trial and error, I found out:
...and that kind of thoroughly sucks. I can remove all the welcome messages so as to allow Safari to at least log on, but then just one user posting a paragraph of text will kick all the Safari users out of the chat room!
Chrome and Firefox don't experience this issue. A while ago I added picture sharing in chat - you send your picture over WebSocket and it echoes it as a data: URL to all the chatters, passing those bytes directly back out; Firefox and Chrome can cope with this perfectly, but that would for sure kick Safari users off for too long of a message!
So, when it comes to Mac OS users I can tell them: Chrome and Firefox work better. But this advice does not fly on iPads or iPhones because, per Apple's rules, web browsers on iOS are not allowed to bring their own browser engines - they all are just custom wrappers around Mobile Safari.
And you guessed it: Mobile Safari doesn't like my WebSockets either!
I am hoping that with EU pressure placed on Apple to where they will allow competing browser engines to join their platform, that at least some of my iOS users will have a way to use my chat room. But how it stands currently is: iPads and iPhones simply can't use my chat room at all, or if they can get on (maybe it's the "too long of message" issue with them as well), they will be fragile and easy to boot offline just by writing too long of a message.
Apple will not innovate on Safari and make it support modern web standards, and they've made sure that nobody else can innovate either. The Blink engine from Chromium and Gecko from Firefox both work great with WebSockets and if only they were allowed to exist in their true forms on Apple mobiles, I wouldn't be ranting about this right now, I could just say "don't use Safari."
And side rant: the reason Apple won't allow Chrome or Firefox to compete with them is because they are scared shitless about Progressive Web Apps, which could compete with their native app store. They won't innovate on Safari at all until their feet are held to the fire (thanks for that as well, EU!), their web browser sucks (as this WebSockets thing illustrates), they're holding everybody back - the new Internet Explorer 6.0!
Even if I owned an iPad, it wouldn't help - you can't get to the browser logs on an iPad browser to even see what kind of error message it's throwing. Though I imagine the error message would be just as helpful as desktop Safari, anyway: "Protocol error."
In order to get logs off an iOS web browser, you need to pair it with a Macbook computer -- the only kind of device that is allowed to run the iOS development kits and is the only way to debug anything that happens on your iPad.
With Mac OS, at least there is a way I can spin up a virtual machine and get my hands on Safari. There is no way to do this for iOS. There's no virtual machine where I can run the genuine Mobile Safari app and have a look at this issue myself. I wish Apple weren't so closed in their ecosystem - comparing it to Android for example, you can debug an Android app using any kind of computer: Windows, Linux, Mac OS, even another Android, even on-device on the same Android.
I am not an iOS developer, I don't care to be an iOS developer, and I don't own any Apple hardware, and it really sucks when I run into a web app issue that should have nothing to do with Apple specific software, and I simply can not even get in and look at the error messages.
I'd been chipping away at this for weeks, basically blindly trying things and throwing shit at the walls and hoping one of my Apple using friends tries my chat room once in a while to see if any of my efforts have worked (spoiler: they haven't worked).
I've also tried reaching out to developers on Mastodon and other social media: my chat room is open source, could somebody with Apple hardware help me debug and see if they can find out what I can do better to get Safari to like my chat room. Maybe I didn't reach the right ears because I've gotten only crickets in response. Meanwhile about a third of my users still can not get onto my chat room at all.
Where I've landed so far is: it seems Safari can connect, but that < 500 character limit issue seems horribly broken and I don't want Safari users getting kicked off left and right by surprise, it's a bad user experience.
If I wait it out long enough (and if the EU is successful), Apple may permit actually good web browser engines on their platform and then my chat will work perfectly on them. It may just take a couple of years though - first Apple would have to be successfully sued into submission, and then Google/Mozilla would have to port their browser engines over which could be its own long tail of development work.
Maybe as a consequence of that regulation, Apple will actually put some new work into Safari instead of just neglecting it and they'll fix their shit. Currently it seems like my WebSocket messages need to be smaller than a tweet on Twitter, and it honestly won't be worth all the effort it would take me to reimagine my whole chat room and come up with a clever protocol to break messages apart into tiny bite sized chunks when it's only one, non-standards compliant web browser, which drags its stick thru the mud as badly as Internet Explorer ever did, that has the issue here.
So are they the new Internet Explorer, or somehow even worse?
I have sometimes had people visit my blog because they were Googling around in general about Apple and they like to fight me in the comments because I dissed their favorite brand. If this is you, at least say something constructive in the comments: have you ever built a WebSockets app and do you have experience to share in how to get Safari to behave? If you're simply an end user fanboy and never installed Xcode in your life, save your comments, please.
Cardell asks:
So this is related to The Breath of the Wild save hacking. I play on the Yuzu emulator now. I just want the Mster Cycle earlyish and fresh vanilla game. Have found a save file editor but it doesn't let you add runes so I can't get the cycle. How did you add it to your save files on the blog? I'm sorry to bother you with something so insignificant but what I'm trying to do is so niche I can't find anything lol
I'm not sure about the Switch version but may have some ideas to get you started.
The savegame editor I used may be for the WiiU only and it provided a simple "Motorcycle" checkbox that adds the rune. If the Switch save editor doesn't do that, but does give you 'advanced' access to the various game flags, maybe setting the flag IsGet_Obj_Motorcycle may do it - the flag is set in my WiiU save files. Or otherwise browse and search around in the flags - there are a lot of them that control all sorts of features in the game, and sometimes they have uintuitive names (IsGet_Obj_RemoteBomb does the bomb rune, IsGet_Obj_StopTimer is the stasis rune, IsGet_Obj_Magnetglove is the magnesis rune, IsGet_Obj_IceMaker for cryonis).
There is also a caveat around runes at all when you're talking very early game: you can hack all these runes in to your profile, but you can't use them in-game until you have picked up a rune yourself. The D-pad shortcut doesn't work otherwise. What I did for my WiiU save files was to:
With the Camera rune added, the D-pad shortcut unlocks and I can now use all of the runes, including the motorcycle, despite never entering one of the Plateau tutorial shrines. (Doing those tutorial shrines would also unlock your rune ability - you just need a rune added "normally" for the tutorial to advance enough to let you use them!)
Good luck!
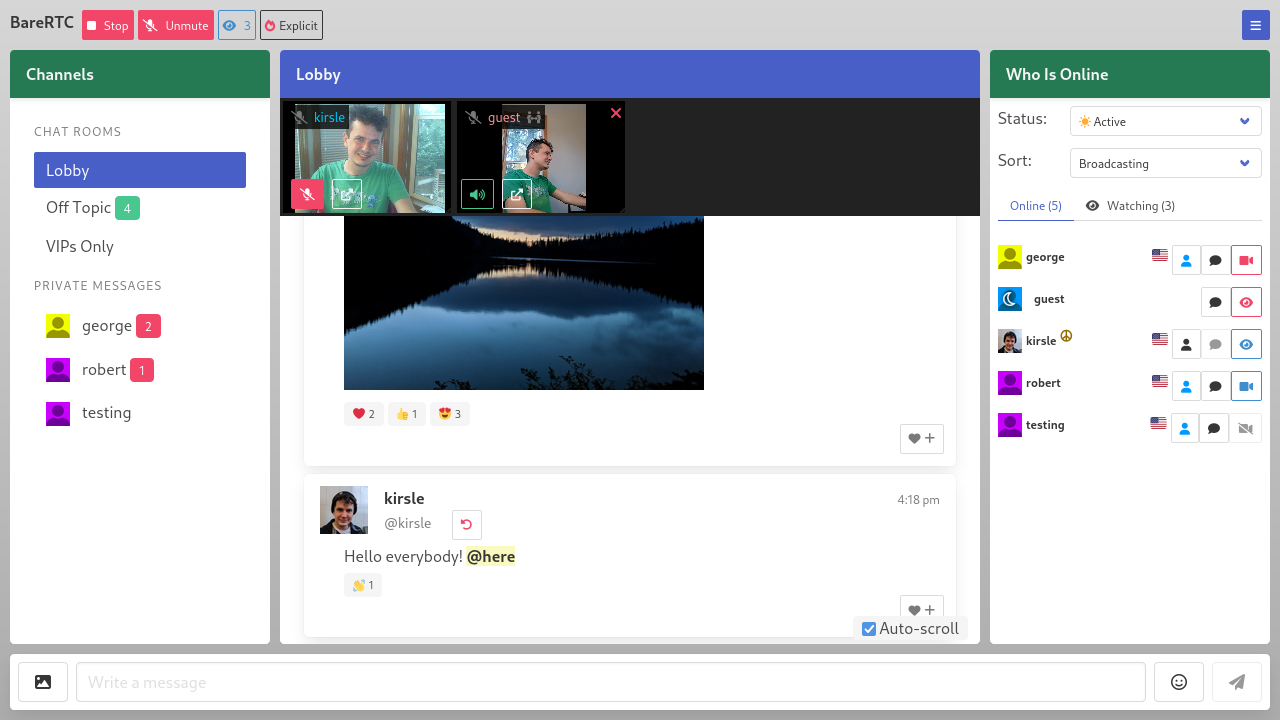
I'm announcing my latest open source project: a WebRTC chat room with asynchronous video support that I'm calling BareRTC. It is very much styled after the classic old-school Flash-based chat rooms that were popular in the early 2000's.
I have a demo of it available here: https://chat.kirsle.net/. I can't guarantee I'll be lurking in that room at any given time but you can test it out yourself on a couple of devices or send the link to some friends and see how it works.
Its primary features are:
The back-end is written in Go and it should easily install onto any server. With WebRTC, the webcam streams are peer-to-peer so you don't need a server in the middle to relay all that video bandwidth (which could be expensive!). Here is a screenshot from the source repo:

In this blog post I'll talk a bit about the technicals and difficulties I ran into getting this app to work.
One of my side projects is nonshy, a social networking site for nudists and exhibitionists. I wanted a chat room for it and I wanted it to work as described above: where some users can be on video but the room isn't all about video and is primarily a text chat room, as not everybody has a camera or the will to be broadcasting on it at all times.
I really expected that a chat room like this should have already existed out there as a free and open source project that I could plug in to my site. There were so many Flash-based rooms just like this in the early 2000's, and WebRTC is a standard web technology now, there are lots of open source apps and libraries that use WebRTC, but none of them worked like these classic old chat rooms did. Most WebRTC apps are in the style of Zoom or Jitsi, where it's expected that all users will be on video.
I didn't want to build my own chat room, but as there was nothing suitable for me to use I had to do it myself. It was a fun learning process to play with WebRTC for the first time.
My chat app now fills the void of such a thing not existing. I didn't want to build it specifically for my social networking site, so it's a stand-alone app that plugs in to any existing userbase by letting your existing site sign a JWT token to authenticate users in. With the JWT you can also convey a profile picture image, profile URL and admin/operator status to the user as they enter the chat.
I named it "BareRTC" for the punny word play: I was "grumpy like a bear" that I had to program this damn thing myself and for the play on words that the itch I was scratching was for a nudist website in particular.
WebRTC is a web standard that allows two browsers to connect to each other (peer-to-peer, ideally) and transmit arbitrary data between them -- usually, video and audio data. Most modern video apps including Zoom, Jitsi Meet, Discord and others are using WebRTC to get video chat to work in a web browser.
The great thing about WebRTC is that it's peer-to-peer so you don't need a server to relay video frames back and forth between users -- saving you a lot of money in bandwidth costs. WebRTC usually works even if both sides of the connection are behind firewalls (such as most home users with a WiFi router that uses NAT). In case neither side can connect to the other, "enterprisey" WebRTC applications will fall back on using a server in the middle to relay video frames back and forth (called a TURN server). My app does not support TURN servers yet, but peer-to-peer video usually works in "most" cases.
These are the things I learned along the way, as this is my very first WebRTC project.
First, the two web browsers need a way to negotiate how they'll connect to one another and what features they will support (data channels, video or audio streams, and which codecs to use with those, and so on). To handle this initial negotiation process, you need a signaling server which is just any server that can echo messages back and forth between the two clients.
My chat room (before adding video support) already had a signaling server: I am using WebSockets to handle the server side of the chat protocol. The web page front-end connects to the WebSockets server to log in with a username and send and receive chat messages.
So I have two users "alice" and "bob" who want to connect peer-to-peer and share video. I programmed my WebSocket server to also be the signaling server for WebRTC: Alice sends a message to my server meant for Bob and my server forwards it along, and the two of them share "ICE candidates" and "SDP messages" back and forth which is how they negotiate how they'll connect to each other (ICE) and what features they will support (SDP). This is the easy part of WebRTC: your back-end signaling server just gives them a method to relay these to each other and then the two browsers have everything they need to (hopefully) establish a peer-to-peer connection directly between themselves.
The part I was getting stuck on the most was that my chat room's video feature is asynchronous: one user is broadcasting a video, and the one who wants to tune in to that might not be broadcasting their own. I could see the ICE and SDP messages being sent between the two users but then nothing would happen: the receiving party was not getting the video streams sent by the caster.
But if the receiver was also casting their own video, the two could connect find and see each other's video!
I found out this is because in the SDP negotiation process, the one connecting (the "offerer") negotiates what features they expect to share, and if they are not sharing their video, they don't request video support; and so the "answerer", even though they added their video streams to the connection, their video is not actually delivered to the offerer.
The fix was that when you called createOffer() you had to say {offerToReceiveVideo: true, offerToReceiveAudio: true} and then all is well.
A crucial part to my success building this app was this barebones WebRTC video chat demo.
It's only 119 lines of basic JavaScript code that quickly gets two browsers into a video call with each other. It uses a service called ScaleDrone for the signaling server (simple channel to allow the ICE/SDP messages to relay between the two browsers). I do not use ScaleDrone in my app but I could see how the JavaScript used it and have my own WebSocket server do the same for my needs.
Some of the quirks that I had to deal with comparing my app to this example were:
My chat room app is released under the GNU General Public License v3 and if you wanted a chat room like this for your website, you're free to check my project out! At some point I may put a mirror to my code on GitHub to allow social development and pull requests for others if you'd like to help improve the feature set.
Check out the source at https://git.kirsle.net/apps/BareRTC
I have just released a new toy program on my website: Error Message Generator 2.0, or ErrorGen for short.
ErrorGen is a simple program that lets a user configure customized error dialog pop-ups, with a custom icon, message and buttons, to prank their friends with or to put to good use by shell scripts if you want to ask the user a quick question from your external program.
My original ErrorGen was inspired by a web tool called "Atom Smasher's Error Message Generator" which would produce images of error dialogs that you could save to disk. My program, however, created "real" dialogs on your desktop PC that you could drag around the screen and interact with. The original version was written using Perl/Tk in 2006 and hasn't been updated a lot since - with the latest release built in 2008 for Windows XP and it hasn't aged well and doesn't run as easily on modern Windows anymore.
In 2022, Atom Smasher's page went offline and I have seen an uptick of interest in my old ErrorGen program ever since: it is recently the #1 most requested page on my website!
So, on January 21, 2023 I decided to reinvent my ErrorGen program from scratch, this time programming it in Go and to explore the Fyne UI toolkit which I had seen around but hadn't played with before. ErrorGen 2.0 has equivalent features to what my original Perl version had, but with a fresh and modern look based on Material Design that comes with Fyne and built for the modern era. I also have some plans to extend ErrorGen 2.0 with new features and especially make it more useful for command line interfaces, to make something on par with GNOME's Zenity tool.
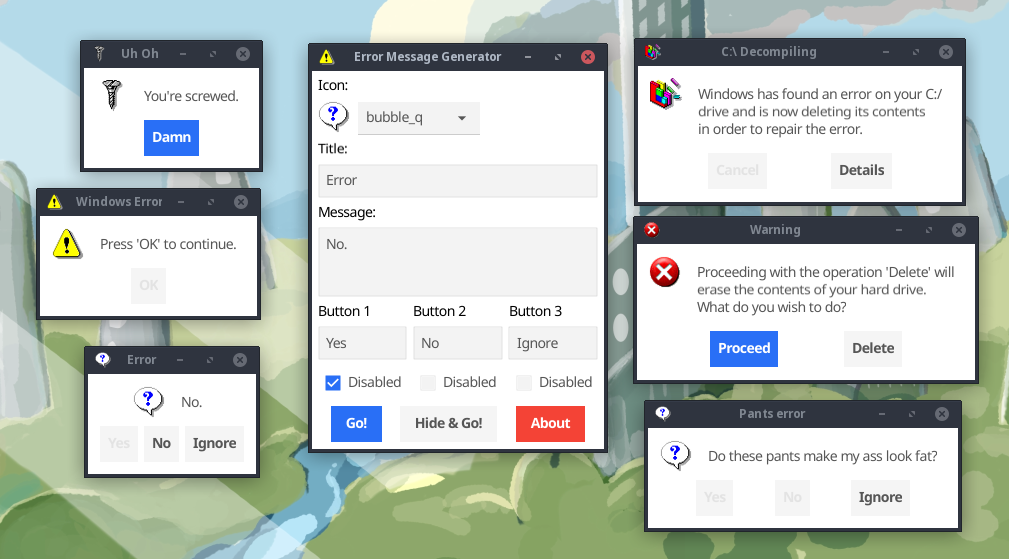
You can check out the new ErrorGen on my Error Message Generator page. The classic Perl version from 2006 is still available here if you want it.
0.0034s.