A discussion thread I got pulled into on Mastodon had me suddenly nostalgic for something we once had on the Internet, and which was really nice while it lasted: the Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol, or XMPP, or sometimes referred to by its original name, Jabber.
What kicked off the discussion was somebody asking about a more modern "decentralized chat platform" known as Matrix (not the movie). A lot of people online talk about how they like Matrix, but I one time had a go at self-hosting my own Matrix node (which I feel I should rant about briefly, below), and the discussion turned back towards something that we used to have which was (in my opinion) loads better, XMPP.
So I haven't posted a good rant on my blog in quite some time - I had chilled out a lot in my older years, but I just have to tell this story about Safari and my struggles in getting it to work with my chat room I had built recently.
My chat room is a fairly basic app - it's open source and written "from scratch" using WebSockets to handle the client/server communication and they pass basic JSON messages around. All fairly standard stuff and shouldn't be a big ask for any modern web browser that supports modern web standards. It works flawlessly in Google Chrome as well as all other Chromium derivatives (including Edge, Brave, etc.), and it works flawlessly on Firefox, and when you run either browser on your Windows, Linux or Mac OS computer. It even works great on all Androids, too - using Chromium or Firefox browser engines.
But then there's Safari. Safari "supports" WebSockets but it doesn't do so very well and I've been fighting this for weeks now trying to chip away at this problem. Both when you run Safari on your Mac OS Ventura desktop or on your iPhone or iPad, Safari is very easy to overwhelm and it will disconnect from the chat room at the slightest hiccup of an issue.
My rant here actually is about three different problems that have made my life difficult trying to get Safari to work:
I don't own a Macbook or an iOS device and so would have no way to even debug or look into this problem, but at least there is an option to run Mac OS inside of a virtual machine (using something like OSX-KVM) so at least I can look into the desktop Safari browser and see what its deal is.
First - here is how my chat basically works: you connect, send your username to log in, the chat tells everyone you joined, sends everyone the new Who's Online roster, and sends some "welcome messages" to the one who joined where I can send my rules or new feature announcements to you.
What I would see when a Safari user logged in was: they'd connect, log in, receive all those welcome messages and then they would immediately hangup the connection and log off. On their side, the web browser gives a very unhelpful error message regarding the WebSocket:
Protocol error.
That's it - it doesn't say what the error was. Even when I have a Safari browser in front of me, they give me no help at all to find out what's wrong!
Through trial and error, I found out:
...and that kind of thoroughly sucks. I can remove all the welcome messages so as to allow Safari to at least log on, but then just one user posting a paragraph of text will kick all the Safari users out of the chat room!
Chrome and Firefox don't experience this issue. A while ago I added picture sharing in chat - you send your picture over WebSocket and it echoes it as a data: URL to all the chatters, passing those bytes directly back out; Firefox and Chrome can cope with this perfectly, but that would for sure kick Safari users off for too long of a message!
So, when it comes to Mac OS users I can tell them: Chrome and Firefox work better. But this advice does not fly on iPads or iPhones because, per Apple's rules, web browsers on iOS are not allowed to bring their own browser engines - they all are just custom wrappers around Mobile Safari.
And you guessed it: Mobile Safari doesn't like my WebSockets either!
I am hoping that with EU pressure placed on Apple to where they will allow competing browser engines to join their platform, that at least some of my iOS users will have a way to use my chat room. But how it stands currently is: iPads and iPhones simply can't use my chat room at all, or if they can get on (maybe it's the "too long of message" issue with them as well), they will be fragile and easy to boot offline just by writing too long of a message.
Apple will not innovate on Safari and make it support modern web standards, and they've made sure that nobody else can innovate either. The Blink engine from Chromium and Gecko from Firefox both work great with WebSockets and if only they were allowed to exist in their true forms on Apple mobiles, I wouldn't be ranting about this right now, I could just say "don't use Safari."
And side rant: the reason Apple won't allow Chrome or Firefox to compete with them is because they are scared shitless about Progressive Web Apps, which could compete with their native app store. They won't innovate on Safari at all until their feet are held to the fire (thanks for that as well, EU!), their web browser sucks (as this WebSockets thing illustrates), they're holding everybody back - the new Internet Explorer 6.0!
Even if I owned an iPad, it wouldn't help - you can't get to the browser logs on an iPad browser to even see what kind of error message it's throwing. Though I imagine the error message would be just as helpful as desktop Safari, anyway: "Protocol error."
In order to get logs off an iOS web browser, you need to pair it with a Macbook computer -- the only kind of device that is allowed to run the iOS development kits and is the only way to debug anything that happens on your iPad.
With Mac OS, at least there is a way I can spin up a virtual machine and get my hands on Safari. There is no way to do this for iOS. There's no virtual machine where I can run the genuine Mobile Safari app and have a look at this issue myself. I wish Apple weren't so closed in their ecosystem - comparing it to Android for example, you can debug an Android app using any kind of computer: Windows, Linux, Mac OS, even another Android, even on-device on the same Android.
I am not an iOS developer, I don't care to be an iOS developer, and I don't own any Apple hardware, and it really sucks when I run into a web app issue that should have nothing to do with Apple specific software, and I simply can not even get in and look at the error messages.
I'd been chipping away at this for weeks, basically blindly trying things and throwing shit at the walls and hoping one of my Apple using friends tries my chat room once in a while to see if any of my efforts have worked (spoiler: they haven't worked).
I've also tried reaching out to developers on Mastodon and other social media: my chat room is open source, could somebody with Apple hardware help me debug and see if they can find out what I can do better to get Safari to like my chat room. Maybe I didn't reach the right ears because I've gotten only crickets in response. Meanwhile about a third of my users still can not get onto my chat room at all.
Where I've landed so far is: it seems Safari can connect, but that < 500 character limit issue seems horribly broken and I don't want Safari users getting kicked off left and right by surprise, it's a bad user experience.
If I wait it out long enough (and if the EU is successful), Apple may permit actually good web browser engines on their platform and then my chat will work perfectly on them. It may just take a couple of years though - first Apple would have to be successfully sued into submission, and then Google/Mozilla would have to port their browser engines over which could be its own long tail of development work.
Maybe as a consequence of that regulation, Apple will actually put some new work into Safari instead of just neglecting it and they'll fix their shit. Currently it seems like my WebSocket messages need to be smaller than a tweet on Twitter, and it honestly won't be worth all the effort it would take me to reimagine my whole chat room and come up with a clever protocol to break messages apart into tiny bite sized chunks when it's only one, non-standards compliant web browser, which drags its stick thru the mud as badly as Internet Explorer ever did, that has the issue here.
So are they the new Internet Explorer, or somehow even worse?
I have sometimes had people visit my blog because they were Googling around in general about Apple and they like to fight me in the comments because I dissed their favorite brand. If this is you, at least say something constructive in the comments: have you ever built a WebSockets app and do you have experience to share in how to get Safari to behave? If you're simply an end user fanboy and never installed Xcode in your life, save your comments, please.
I'm announcing my latest open source project: a WebRTC chat room with asynchronous video support that I'm calling BareRTC. It is very much styled after the classic old-school Flash-based chat rooms that were popular in the early 2000's.
I have a demo of it available here: https://chat.kirsle.net/. I can't guarantee I'll be lurking in that room at any given time but you can test it out yourself on a couple of devices or send the link to some friends and see how it works.
Its primary features are:
The back-end is written in Go and it should easily install onto any server. With WebRTC, the webcam streams are peer-to-peer so you don't need a server in the middle to relay all that video bandwidth (which could be expensive!). Here is a screenshot from the source repo:
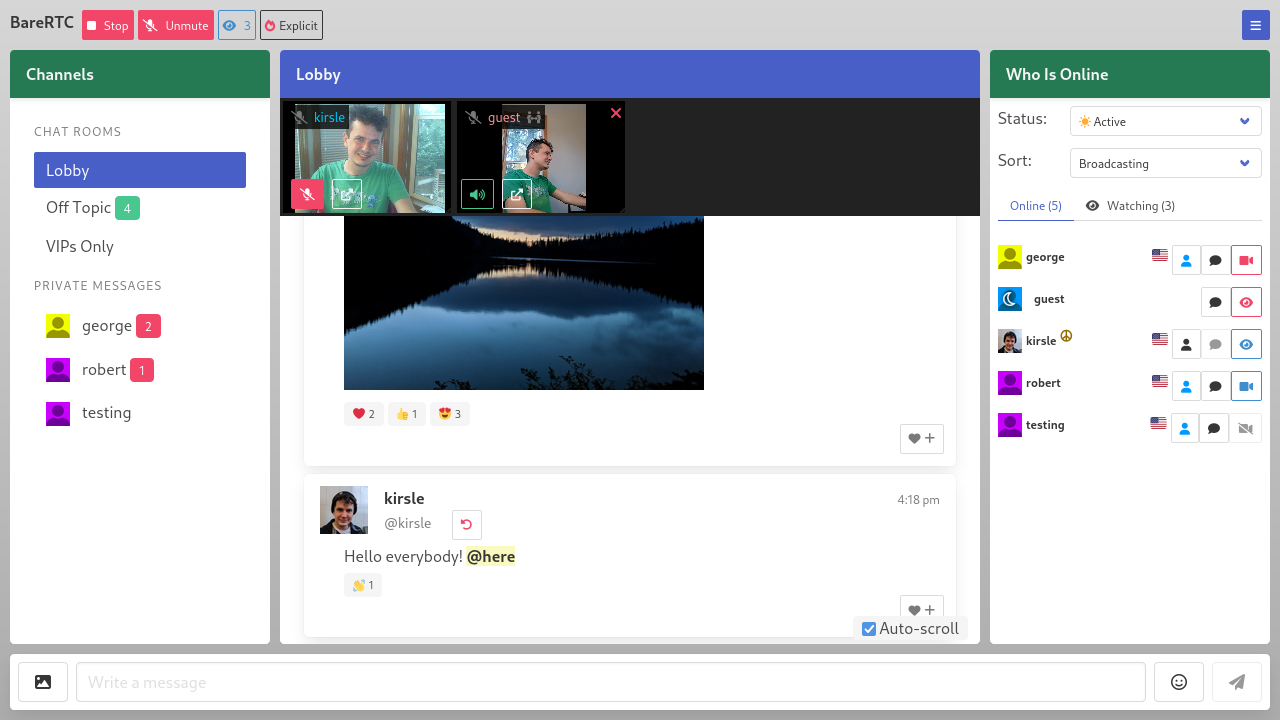
In this blog post I'll talk a bit about the technicals and difficulties I ran into getting this app to work.
One of my side projects is nonshy, a social networking site for nudists and exhibitionists. I wanted a chat room for it and I wanted it to work as described above: where some users can be on video but the room isn't all about video and is primarily a text chat room, as not everybody has a camera or the will to be broadcasting on it at all times.
I really expected that a chat room like this should have already existed out there as a free and open source project that I could plug in to my site. There were so many Flash-based rooms just like this in the early 2000's, and WebRTC is a standard web technology now, there are lots of open source apps and libraries that use WebRTC, but none of them worked like these classic old chat rooms did. Most WebRTC apps are in the style of Zoom or Jitsi, where it's expected that all users will be on video.
I didn't want to build my own chat room, but as there was nothing suitable for me to use I had to do it myself. It was a fun learning process to play with WebRTC for the first time.
My chat app now fills the void of such a thing not existing. I didn't want to build it specifically for my social networking site, so it's a stand-alone app that plugs in to any existing userbase by letting your existing site sign a JWT token to authenticate users in. With the JWT you can also convey a profile picture image, profile URL and admin/operator status to the user as they enter the chat.
I named it "BareRTC" for the punny word play: I was "grumpy like a bear" that I had to program this damn thing myself and for the play on words that the itch I was scratching was for a nudist website in particular.
WebRTC is a web standard that allows two browsers to connect to each other (peer-to-peer, ideally) and transmit arbitrary data between them -- usually, video and audio data. Most modern video apps including Zoom, Jitsi Meet, Discord and others are using WebRTC to get video chat to work in a web browser.
The great thing about WebRTC is that it's peer-to-peer so you don't need a server to relay video frames back and forth between users -- saving you a lot of money in bandwidth costs. WebRTC usually works even if both sides of the connection are behind firewalls (such as most home users with a WiFi router that uses NAT). In case neither side can connect to the other, "enterprisey" WebRTC applications will fall back on using a server in the middle to relay video frames back and forth (called a TURN server). My app does not support TURN servers yet, but peer-to-peer video usually works in "most" cases.
These are the things I learned along the way, as this is my very first WebRTC project.
First, the two web browsers need a way to negotiate how they'll connect to one another and what features they will support (data channels, video or audio streams, and which codecs to use with those, and so on). To handle this initial negotiation process, you need a signaling server which is just any server that can echo messages back and forth between the two clients.
My chat room (before adding video support) already had a signaling server: I am using WebSockets to handle the server side of the chat protocol. The web page front-end connects to the WebSockets server to log in with a username and send and receive chat messages.
So I have two users "alice" and "bob" who want to connect peer-to-peer and share video. I programmed my WebSocket server to also be the signaling server for WebRTC: Alice sends a message to my server meant for Bob and my server forwards it along, and the two of them share "ICE candidates" and "SDP messages" back and forth which is how they negotiate how they'll connect to each other (ICE) and what features they will support (SDP). This is the easy part of WebRTC: your back-end signaling server just gives them a method to relay these to each other and then the two browsers have everything they need to (hopefully) establish a peer-to-peer connection directly between themselves.
The part I was getting stuck on the most was that my chat room's video feature is asynchronous: one user is broadcasting a video, and the one who wants to tune in to that might not be broadcasting their own. I could see the ICE and SDP messages being sent between the two users but then nothing would happen: the receiving party was not getting the video streams sent by the caster.
But if the receiver was also casting their own video, the two could connect find and see each other's video!
I found out this is because in the SDP negotiation process, the one connecting (the "offerer") negotiates what features they expect to share, and if they are not sharing their video, they don't request video support; and so the "answerer", even though they added their video streams to the connection, their video is not actually delivered to the offerer.
The fix was that when you called createOffer() you had to say {offerToReceiveVideo: true, offerToReceiveAudio: true} and then all is well.
A crucial part to my success building this app was this barebones WebRTC video chat demo.
It's only 119 lines of basic JavaScript code that quickly gets two browsers into a video call with each other. It uses a service called ScaleDrone for the signaling server (simple channel to allow the ICE/SDP messages to relay between the two browsers). I do not use ScaleDrone in my app but I could see how the JavaScript used it and have my own WebSocket server do the same for my needs.
Some of the quirks that I had to deal with comparing my app to this example were:
My chat room app is released under the GNU General Public License v3 and if you wanted a chat room like this for your website, you're free to check my project out! At some point I may put a mirror to my code on GitHub to allow social development and pull requests for others if you'd like to help improve the feature set.
Check out the source at https://git.kirsle.net/apps/BareRTC
I have just released a new toy program on my website: Error Message Generator 2.0, or ErrorGen for short.
ErrorGen is a simple program that lets a user configure customized error dialog pop-ups, with a custom icon, message and buttons, to prank their friends with or to put to good use by shell scripts if you want to ask the user a quick question from your external program.
My original ErrorGen was inspired by a web tool called "Atom Smasher's Error Message Generator" which would produce images of error dialogs that you could save to disk. My program, however, created "real" dialogs on your desktop PC that you could drag around the screen and interact with. The original version was written using Perl/Tk in 2006 and hasn't been updated a lot since - with the latest release built in 2008 for Windows XP and it hasn't aged well and doesn't run as easily on modern Windows anymore.
In 2022, Atom Smasher's page went offline and I have seen an uptick of interest in my old ErrorGen program ever since: it is recently the #1 most requested page on my website!
So, on January 21, 2023 I decided to reinvent my ErrorGen program from scratch, this time programming it in Go and to explore the Fyne UI toolkit which I had seen around but hadn't played with before. ErrorGen 2.0 has equivalent features to what my original Perl version had, but with a fresh and modern look based on Material Design that comes with Fyne and built for the modern era. I also have some plans to extend ErrorGen 2.0 with new features and especially make it more useful for command line interfaces, to make something on par with GNOME's Zenity tool.
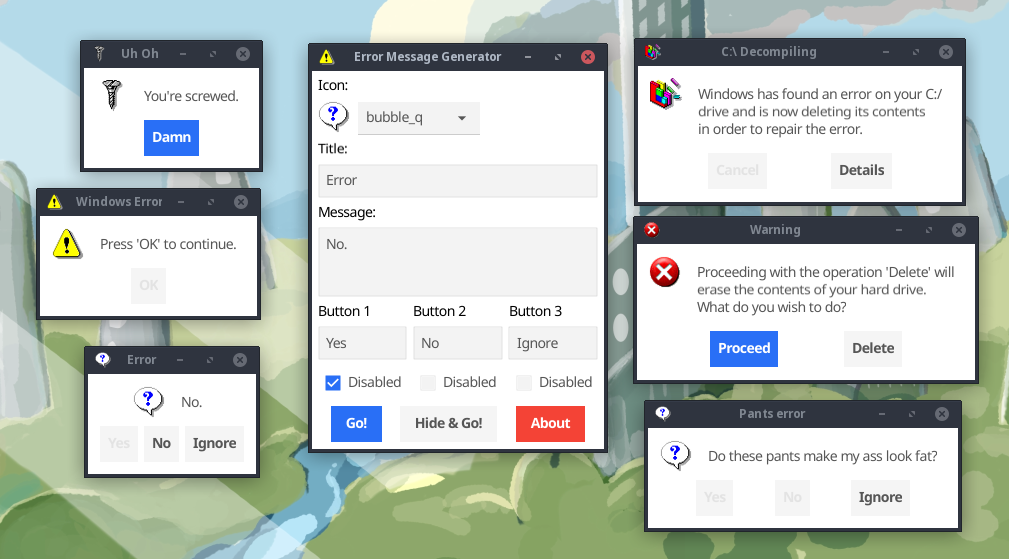
You can check out the new ErrorGen on my Error Message Generator page. The classic Perl version from 2006 is still available here if you want it.
Is Zenmsg a virus? asks:
It only opened a command box, and nothing else happened. Is this a virus?
No, it's not. 😊 ZenMsg is a command-line program (so it opens your DOS prompt if double-clicked on), but it requires command-line options to tell it what to do. When run without any options, it prints its usage information to the terminal and then exits; so when double-clicked on, your DOS prompt appeared and then closed because ZenMsg exited.
You'll want to run it from a PowerShell or Command Prompt window first (so that the console sticks around after the program exits), and you can see it just prints its usage information:
C:\Users\Noah\Downloads> ZenMsg.exe
Usage:
ZenMsg [--error --alert --info --question]
[--title] [--text] [--button label]
[--icon name_or_file]
[--default label] [--cancel label]
[--disabled n]
[--version] [--help]
Use the "--help" option for more help.
(and it goes into detail on all the options)
If you call it with ZenMsg --help it goes into full detail (the same documentation that's in the ZenMsg.html page the program ships with), including all the names of built-in icons. Every icon available on the Error Message Generator is built in to ZenMsg, and you can point it to a custom image on disk to use your own icon:
BUILT-IN ICONS
Here is a list of all the built-in icons that you can use by name:
aim_guy - Blue AIM guy icon
aol_icon - Blue AOL icon
attention - Yellow triangle around an exclamation mark
bomb - Round black bomb icon
bomb_dynamite - Icon of a bundle of dynamite and a trigger
bomb_grenade - Icon of a grenade
bulb - White light bulb
butterfly - MSN Butterfly icon
cake - Slice of pink cake on a blue plate
circularsaw - Icon of a handheld circular saw
control_panel - Generic control panel icon
cow - Icon of a cow and a computer tower
defrag - Disk Defragmenter icon
disk_blue - Generic blue floppy disk icon
disk_blue_label - Blue floppy disk with a label
disk_orange - Generic orange floppy disk
disk_red - Generic red floppy disk
disk_red_label - Red floppy disk with a label
disk_skull - Gray floppy disk with skull and crossbones
disk_yellow - Generic yellow floppy disk
error - Old-school X in a red circle error dialog icon
error2 - Modern, shiny incarnation of an error dialog icon
error3 - Beveled error dialog icon (like Windows XP)
error4 - A red X icon
file_cabinet - File cabinet icon
find - Find Files icon
floppy_drive - Generic floppy drive icon
fortunecookie - Icon of a fortune cookie
garbage_empty - Empty garbage can
garbage_full - Bloated garabage can
gun - Icon of a revolver pistol
hammer - Icon of a hammer
heart - Icon of a shiny red heart
help - Old-school Windows Help icon
hub - Icon of a hardware hub of sorts (networking?)
hwinfo - Icon of a PCI device with blue "i" bubble above it
ie5 - Icon of old-school Internet Explorer
info - Speech bubble with an "i" inside
keys - Generic icon of keys
keys2 - Old Windows key icon
keys3 - Generic key and padlock icon
labtec - Icon of a server or something?
mac - Striped colorful Apple logo
mail - Generic icon of an envelope
mail_deleted - Same envelope with a red X emblem in the corner.
mailbox - Mailbox with the flag down
mouth - Smiling mouth icon
msdos - MS-DOS icon
mycomputer - A "My Computer" icon
mycomputer2 - A "My Computer" icon
mycomputer3 - A "My Computer" icon
newspaper - Generic newspaper icon
peripheral - Generic computer peripheral icon
plant_leaf - A certain green leafy plant
pocketknife - A swiss army pocket knife
question - Icon of a speech bubble with a "?" inside
radiation - Yellow and black radiation symbol
ram - Icon of a couple sticks of RAM
recycle - Green recycle arrows logo
recycle2 - Recycle arrows enveloping a globe of Earth
scanner - Generic scanner icon
screw - Golden screw icon
screw2 - Gray screw icon
setup - Generic icon for "setup.exe" type programs
skull - Black skull and crossbones
skull2 - Picture of a skull
skull3 - White skull and crossbones
tux - Icon of our favorite Linux mascot
tux_config - Tux dressed up like a repairman
ups - Icon of an uninterruptible power supply
zipdisk - Icon of a single zip disk
zipdisks - Icon of numerous zipdisks
You can call ZenMsg from a batch file or any other program (e.g. a Python or Perl script could call ZenMsg.exe and send it parameters). For example, open Notepad and save the following as "example.bat" (with quotes, ensuring that it gets a .bat extension and not .bat.txt) and place it in the same folder next to ZenMsg.exe:
@echo off
ZenMsg --alert --title "Critical Error" --text "Now you've done it." ^
--button "Ok" --button "Cancel" --button "Accept blame" ^
--disabled 1 --disabled 2 > zenmsg-answer.txt
echo The user had selected:
type zenmsg-answer.txt
del zenmsg-answer.txt
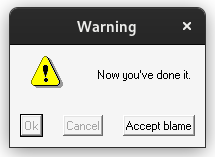
Double-clicking your example.bat file would then pop up that alert box. ZenMsg prints the user's selected button to its standard output, which we captured above by piping it into zenmsg-answer.txt (it's possible to get output from commands in e.g. Perl scripts too, so your program can ask the user a question and then have branching behavior depending on which button the user clicked on).
On forums like r/privacy people often discuss the role of open source software when it comes to privacy and end-to-end encrypted messaging applications. The general consensus is: a privacy focused app must be open source so that people can get their eyes on the source code and audit it for security vulnerabilities, verify it's doing what it says in the tin and without any secret government backdoors built in that would undermine the security and reveal peoples' private chats.
These are all well and good: if the source code is not open, you can't verify the code isn't doing something sneaky like uploading your encryption keys to the service provider or whatever. But, open source alone isn't a silver bullet to help guarantee the security of the app:
In this post I'll address a few common tired things I hear people on r/privacy say in regards to this topic and how it's never quite that simple.
In this blog post, I'll recount my experience in web development over the last 20 years and how the technology has evolved over time. From my early days of just writing plain old HTML pages, then adding JavaScript to those pages, before moving on to server-side scripts with Perl (CGI, FastCGI and mod_perl), and finally to modern back-end languages like Python, Go and Node.js.
Note that this primarily focused on the back-end side of things, and won't cover all the craziness that has evolved in the front-end space (leading up to React.js, Vue, Webpack, and so on). Plenty has been said elsewhere on the Internet about the evolution of front-end development.
I first started writing websites when I was twelve years old back around the year 1999. HTML 4.0 was a brand new specification and the common back-end languages at the time were Perl, PHP, Coldfusion and Apache Server Side Includes.
I added a new feature to my Go blog app that sort of automates a Tumblr-style "Ask Me" feature, which I found useful for other blogs I run on this codebase.
So Kirsle.net has gained an ask me anything page. It's like a Contact Me form except your question will become a blog post with my answer attached and you might receive a notification e-mail if you want.
As of a few minutes ago, I've swapped out the Python backend of Kirsle.net with a new Go backend that I've been rewriting from scratch the past few months.
The Go codebase is a little rough around the edges and I'll be refactoring it over time. This is the first blog post on the new platform, so let me tell you about my open source Go blog!
I was reading this ACLU blog post about how DreamHost was served with a warrant to hand over IP addresses of some 1.3 million visitors to a website they host, and it got me thinking: do websites really need to store IP addresses of their visitors?
There are a lot of VPN companies such as Private Internet Access that advertise far and wide that they explicitly chose not to keep any logs. The idea is that if the VPN provider is served with a warrant for user activity, they would have no data to hand over, because they never stored anything in the first place. Why don't websites do that?
0.0020s.